The Mysteries of the Arctic: Exploring the Remote Location is 65.476721-173.511416.-1125
In today’s interconnected world, geographical locations play a crucial role in various aspects of life. From navigation systems to scientific research, understanding precise coordinates can make a significant difference in different fields. The location associated with the coordinates 65.476721-173.511416.-1125 has raised curiosity due to its remote and seemingly isolated placement.
Understanding Coordinates and Their Importance
Before diving into the specific location, let’s briefly revisit what coordinates represent. Geographic coordinates, like 65.476721 and 173.511416, are a way to pinpoint exact locations on Earth. They are part of the geographic coordinate system, which uses latitude and longitude to describe a location.
- Latitude: This number, 65.476721, refers to how far north or south a location is from the Equator. The value suggests that the location is quite far north, placing it well into the Arctic region.
- Longitude: This number, 173.511416, describes how far east or west the location is from the Prime Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England. With a positive value, we know the location lies east of this point, specifically in the Far Eastern region of Russia.
When combined, these coordinates describe a very remote and cold region of the planet. But what exactly can we find there?
Location Overview: 65.476721-173.511416.-1125
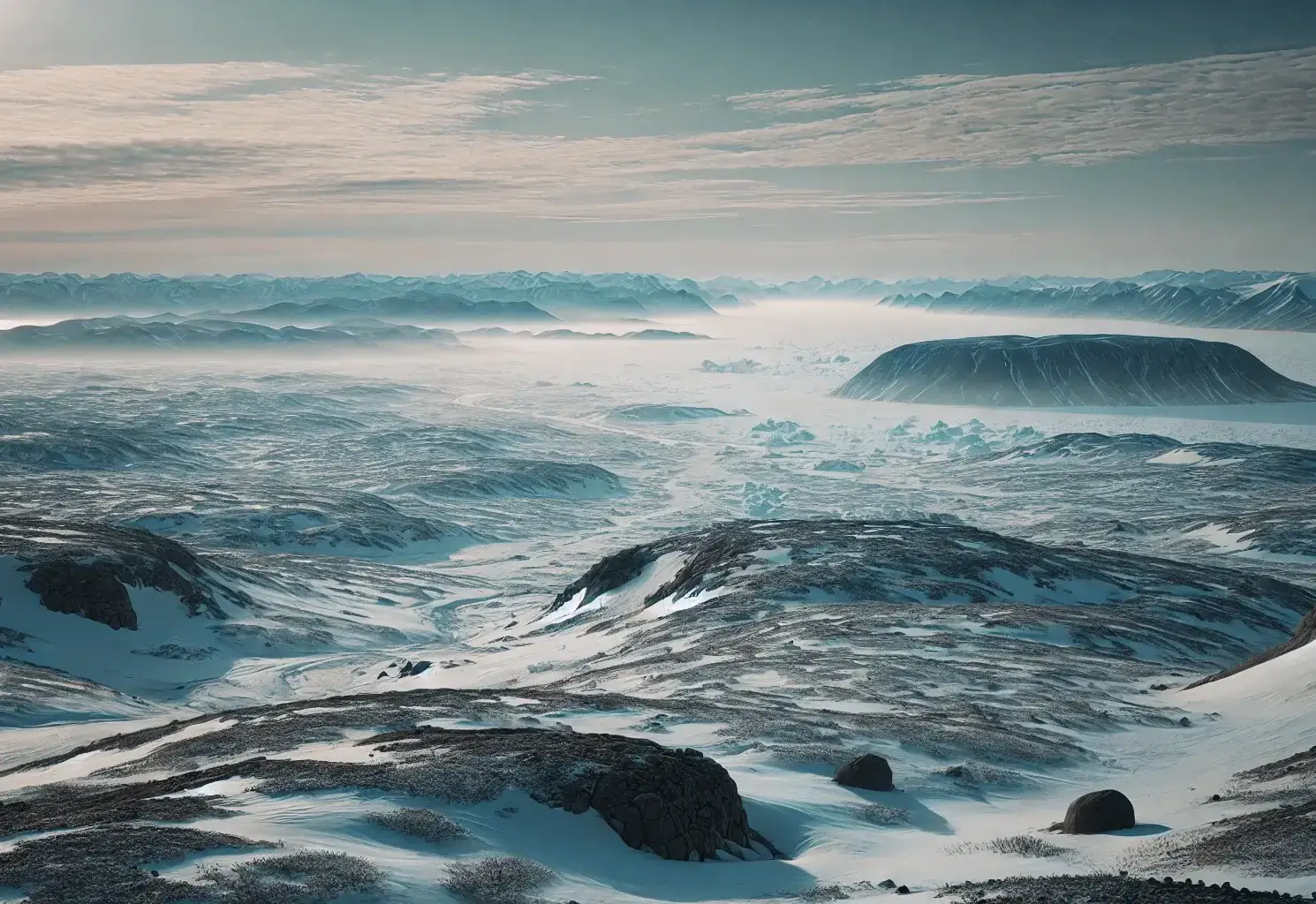
The coordinates 65.476721 – 173.511416 place this location in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, which is in Russia’s Far East. This area is known for its extreme Arctic climate, sparse population, and rugged landscapes. Specifically, this location is near the coast of the Chukchi Sea, part of the Arctic Ocean.
Geographic Characteristics
The location sits within the Arctic Circle, a region that is known for its cold climate and unique environmental conditions. The Chukchi Sea, which borders this location, remains frozen for most of the year. The terrain surrounding these coordinates includes tundra landscapes with very little vegetation due to the harsh climate. The soil is often frozen in a condition known as permafrost.
This area is also characterized by:
- Harsh Winters: Temperatures in this region can drop to extremely low levels, often falling below -30°C during the long winter months.
- Short Summers: The summers are brief and cool, with average temperatures barely exceeding 10°C. However, during this time, the sun does not set for several weeks, creating the famous phenomenon known as the Midnight Sun.
- Limited Vegetation: Due to the freezing temperatures and permafrost, only hardy plants like mosses, lichens, and small shrubs can survive in this area.
Human Presence in the Area
The location 65.476721-173.511416.-1125 is extremely remote, with very little human activity. The closest inhabited area is the small town of Pevek, one of the northernmost settlements in Russia, which is over 100 kilometers away from this coordinate.
Indigenous Populations
Chukotka is home to indigenous peoples such as the Chukchi and Yupik. These indigenous groups have historically lived in harmony with the Arctic environment, relying on fishing, hunting, and reindeer herding to sustain their communities. Although many indigenous people have moved to more urban areas, some still live in traditional ways, navigating the challenging Arctic conditions.
Scientific Research
The Arctic is a hotspot for scientific research, especially in the fields of climate change, glaciology, and biology. While there may not be permanent scientific stations at these exact coordinates, researchers frequently visit the Arctic region to study permafrost, sea ice, and the effects of climate change. The remoteness of the location makes it a valuable site for collecting data with minimal human interference.
Military Presence
Due to its strategic location in the Arctic, Russia maintains a military presence in the wider region, including Chukotka. The Arctic is of growing geopolitical interest, as melting ice opens up new shipping routes and opportunities for resource extraction. While there may not be military bases at the exact coordinates 65.476721-173.511416.-1125, the broader region is part of Russia’s Northern Fleet operations, which monitors Arctic waters and airspace.
Environmental and Ecological Importance
The Arctic, including the area around 65.476721-173.511416.-1125, is an ecologically sensitive region. Its frozen seas and tundra landscapes are home to a variety of wildlife species that have adapted to survive in extreme conditions.
Wildlife in the Region
Some of the species that can be found near this location include:
- Polar Bears: These iconic Arctic predators roam the ice sheets and coastal areas in search of seals, their primary food source. The Chukchi Sea is a critical habitat for polar bears, especially as the ice continues to retreat due to climate change.
- Arctic Foxes: These small mammals are well-adapted to the cold and can be found hunting for small rodents and birds in the tundra.
- Seabirds: Numerous seabirds, including puffins and guillemots, nest along the cliffs of the Chukchi Sea coast during the short summer season.
- Marine Life: The waters of the Chukchi Sea are rich in marine life, including seals, walruses, and various species of fish. During the summer, bowhead whales and belugas can be seen migrating through the region.
Climate Change Impact
The Arctic is one of the regions most affected by climate change, with temperatures rising at twice the global average rate. As a result, the ice cover in the Chukchi Sea and surrounding areas is retreating rapidly, causing profound changes in the ecosystem.
The melting ice is having a significant impact on wildlife. For instance, polar bears are struggling to find enough sea ice to hunt for seals, which has led to population declines in some areas. Additionally, indigenous communities that rely on ice for hunting and travel are finding it more difficult to maintain their traditional way of life.
Strategic Importance of the Location
As the Arctic ice continues to melt, new shipping routes are opening up through the Arctic Ocean. The Northern Sea Route, which passes along the coast of Russia, including the region near 65.476721-173.511416.-1125, is becoming increasingly viable for commercial shipping. This route is much shorter than traditional routes through the Suez Canal, potentially reducing shipping times between Europe and Asia.
In addition to shipping, the Arctic is thought to contain vast reserves of natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. The area around Chukotka and the Chukchi Sea could become a focal point for resource extraction in the future, although the environmental risks of such activities are significant.
Challenges of the Region
Despite its potential, the Arctic remains one of the most challenging environments for human activity. The extreme cold, remote location, and lack of infrastructure make it difficult to establish permanent settlements or industrial operations.
- Logistical Difficulties: Transporting equipment and supplies to such a remote location is expensive and time-consuming. The nearest major cities are thousands of kilometers away, and there are few roads or airstrips in the region.
- Environmental Concerns: Any large-scale human activity in the region, such as mining or oil drilling, could have devastating effects on the fragile Arctic ecosystem. Oil spills, for example, would be incredibly difficult to clean up in such a remote and icy environment.
Conclusion
The location 65.476721-173.511416.-1125 is a remote and isolated point in the Arctic region of Russia, specifically in Chukotka. This area, marked by its harsh climate, minimal human presence, and unique ecological characteristics, holds significance in terms of environmental research and potential geopolitical interests. While the site itself may not have permanent settlements or industrial activity, it sits within a broader context of Arctic exploration and the challenges associated with this fragile environment.
For more information visit: The Readings Hub